High Speed Pipe
In a redundant "High Availability" (HA) system (requires package 410), there are two cores: one Active, and one Standby. A 'High Speed Pipe' (HSP) connects the cores, in addition to the ELAN, to synchronise memory, disk, health count, and heartbeat information.
The HSP is 'plug-and-play'. Once connected (HSP/LAN2), it will immediately start looking for a heartbeat from the other core.
- If a second core is detected, both the cores negotiate to determine 'Active' and 'Standby' roles.
- If a call server cannot detect the other core, it will boot as a Single Core (non-redundant) system.
HSP ports must be at least 100 Mbps, and full duplex, connected via a CAT-5e / CAT-6 cross-over cable (max. length 100m).
Default HSP IP addresses, it is normally not necessary to change these:
- Core 0:
127.2.0.1 - Core 1:
127.2.0.2
A dedicated VLAN may also be used for the HSP. It must be non-routed, and separate to the ELAN subnet. The round trip delay must be less than 30 msec, and packet loss below 0.1 %. From Rel. 4.5, the default HSP IP addresses can changed in LD 117:
=> new host DEV_SIDE0_HSP 10.10.10.10 ⇐ the host names are fixed, NEW or OUT, not CHG INET Data Added => new host DEV_SIDE1_HSP 10.10.10.11 INET Data Added => chg hsp_mask 255.255.255.252 INET Data Changed => set hsp_ip ⇐ SET to activate the new HSP IP settings Activating HSP Addresses. Please wait ...
LD 137: stat hsp shows the 'active' values, LD 117: prt host & prt hsp_mask shows the 'configured' values.
Ports should always be set to auto-negotiate. Confirm that speed and duplex match with LD 137: STAT HSP.
ld 137 CIOD000 .stat hsp LCS HSP STATE is UP ⇐ UP is good, DOWN is not HSP LINK CARRIER: OK Auto Negotiation: Enabled Actual Line Speed: 1000 Mbps ⇐ CP PII = 100 Mbps Actual Duplex Mode: Full Duplex ⇐ must be full-duplex
HSP Troubleshooting:
If one of the following occurs:
- Call Servers do not perform graceful switchover and/or come up as single CPUs
- Disk sync and mem sync take a long time (greater than 10 minutes)
Then check the following:
- CP PII: verify any LAN equipment connected to the HSP is hard-coded to 100 Mbps full duplex.
- CP PIV: check speed, and for a duplex mismatch. A duplex mismatch may work, but not very well.
- If the HSP connects via a switch, make sure is on its own VLAN, and that 802.1 is configured correctly.
CPPM Call Servers:
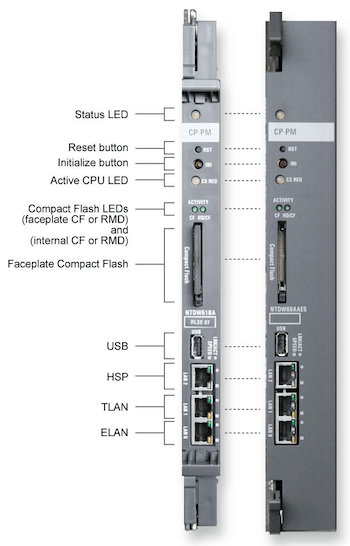
CPPM cards can operate in Single (SA) or Dual (HA) CPU mode.
Call Server mode and redundancy status is shown by a tri-color "CS RED" LED:
CS RED Status Redundant mode, Active CS Redundant mode, Standby CS Redundant mode, Fault (HSP down) Standard mode (Single CPU Mode)
By default the HSP network interface (LAN2) is set to auto-negotiate.
The LAN port LED's indicate:
LED 2 (top) No Link, No Activity Link Valid Link Valid, Activity LAN 2
LED 1 (bottom) 10 Mbps 100 Mbps 1000 Mbps
CPU Maintenance:
LD 135 - Useful Commands:
Command Description STAT CPU Get the status and core numbers for both CPUs. See below. SPLIT Put a redundant (shadowed) system into single (non-shadowed) mode JOIN 1. Restores redundancy to a system put in single mode by the SPLIT command.
2. Synchronizes the processor's memory and drives.
Note: This command can only be used if the system is in single mode (SPLIT).CUTOVR Force transfer of call processing from active core to standby core SCPU Gracefully switch cores
LD 135 - STAT CPU Example:
Normal is: 1 enabled (active) and 1 standby (inactive) core, redundant system and disk state, same health.
.stat cpu cp 0 1 PASS -- ENBL ⇐ Call Processor 0 SYSTEM STATE = REDUNDANT DISK STATE = REDUNDANT HEALTH = 14 VERSION = Nov 16 2010, 14:42:29 Side = 0, DRAM SIZE = 1006 MBytes CP[0] located at IPMG [4 0 1] cp 1 1 PASS -- STDBY ⇐ Call Processor 1 SYSTEM STATE = REDUNDANT DISK STATE = REDUNDANT HEALTH = 14 VERSION = Nov 16 2010, 14:42:29 Side = 1, DRAM SIZE = 1006 MBytes CP[1] located at IPMG [8 0 1]
The following indicates a problem with the HSP:
.stat cpu cp 0 1 PASS -- ENBL ⇐ Call Processor 0 is active SYSTEM STATE = SPLIT (HSP DOWN) DISK STATE = SPLIT : cp 1 1 UNKNOWN PASS -- STDBY ⇐ Call Processor 1 is not available SYSTEM STATE = NOT AVAILABLE DISK STATE = NOT AVAILABLE :
LD 135 STAT states:
CP STATE:
| PASS -- ENBL | Call Processor is running, and Active |
| PASS -- STDBY | Call Processor is running, in Standby |
| DSBL: NOT RESPONDING | Call Processor is not accessible/faulty |
SYSTEM STATE:
| REDUNDANT | Both CPUs are up and actively communicating with each other. Disk and memory shadowing are complete. |
| SPLIT HSP DOWN | The redundant system is split (the split command has been issued). Both CPUs are communicating over the ELAN but disk and memory shadowing between the two CPUs is not synchronized. |
| SPLIT HSP UP | The redundant system is up, but has been manually split by issuing the split command in LD 135. |
| REDUNDANT HSP DOWN | The system is redundant, but the HSP is down. Both CPUs are communicating over the ELAN, but disk and memory shadowing between the two CPUs is not synchronized. INI'ing the inactive core my resolve this. |
| SYNCING | The system is not redundant, but disk and memoring shadowing between the two CPUs is in progress. |
| SINGLE | The system does not have a redundant CPU, or the ELAN and HSP to the redundant CPU are disconnected. |
DISK STATE:
| SPLIT | This indicates that the SPLIT command has been issued in LD 135. |
| REDUNDANT | This indicates that the JOIN command has been issued in LD 135. |
HEALTH:
| HEALTH = XX | This indicates the relative health of each CPU, the maximum value depends on configuration. If a CPU has problems with hardware or network connectivity it's health count will go down. Both CPU health count values should be equal, otherwise the 'healthier core' is nominated as the active CPU, and a switchover occurs. Two Signaling Servers are required for health monitoring to work. |

