Fax Issues with MGC's
Fax settings and performance over VoIP solutions vary depending on the network configuration. In order to achieve a successful faxing environment the VoIP solution has to be engineered properly. Following are configuration and network design aspects that need to be taken into consideration when implementing faxing in VoIP solutions:
CODECs:
T.38:
- Older fax machines use V.21
- For lower speeds (V.21) protocol T.38 should be used in the VoIP segments of the call.
Modem Pass Through (G.711):
- Newer fax machines use Modem Protocols to achieve higher speeds (V.34).
- The Modem pass through feature is intended for modems and high speed faxes employing V.34. It uses clear channel G.711 over the VoIP segments of the call.
Modem Pass Through:
The Modem Pass Through feature will detect the phase reversal tone negotiation used for higher speeds and will tell the DSPs involved in the call to disable echo-cancellation and all other non linear components.
- The CLS MPTD should be used for analog fax lines. It allows the DSPs to change between T.38 for lower speeds and G711 for higher speeds (support for T.38 and V.34 faxes).
- The CLS MPTA should be used only for Modems. It will force all calls to use G711. When going to the PSTN we have no control over the far end, however speeds of 33.6 kbit/s should be achievable.
 Faxing at 33.6 requires all network elements to support it. When high speed connections cannot be made with a consistent success rate, it is recommended to set the fax units to a maximum speed of 14.4.
Faxing at 33.6 requires all network elements to support it. When high speed connections cannot be made with a consistent success rate, it is recommended to set the fax units to a maximum speed of 14.4.Supported Scenarios:
TL;DR: An analog fax should use analog trunks in the same MGC, but can use digital trunks in any MGC.
- Two faxes connected to analog lines:
 in the same MGC (TDM call, no DSPs used)
in the same MGC (TDM call, no DSPs used)
 in different MGCs of the same CS1K (DSPs are used)
in different MGCs of the same CS1K (DSPs are used)
- One fax connected to an analog line in an MGC, to:
 IP Trunk to a remote system with a fax (DSPs are used)
IP Trunk to a remote system with a fax (DSPs are used)
 Analog trunk in same MGC to PSTN fax (No DSPs are involved)
Analog trunk in same MGC to PSTN fax (No DSPs are involved)
 Analog trunk in different MGC of the same CS1K to PSTN fax
Analog trunk in different MGC of the same CS1K to PSTN fax
 Digital trunk in same MGC to PSTN fax (No DSPs are involved)
Digital trunk in same MGC to PSTN fax (No DSPs are involved)
 Digital trunk in different MGC of the same CS1K to PSTN fax (DSPs are used)
Digital trunk in different MGC of the same CS1K to PSTN fax (DSPs are used)
Data Network:
Depending on the scenario, fax calls can traverse the IP network either internally (ex: MGC to MGC) or externally (ex: IP Trunks).
It is important to engineer the data network to support the following:
Media card configuration:
- G.711/T.38 codecs
- 20 ms packet size
- Round trip delay must be less than 50 ms
- Packet loss must be less than 0.5%
- V.34 rate (33.6 kbit/s) as long as far end supports Modem Pass Through feature
- Mean Jitter is less than 5 ms
Performance degrades significantly with packet loss (which must be less than 0.5%), when the delay (round trip) is greater than 50 msec, and when mean jitter is greater than 5msec.
 Avaya does not guarantee that all fax brands will operate properly over all G.711 (VoIP) networks. Before you deploy faxes, test the fax within the network to verify reliable operation.
Avaya does not guarantee that all fax brands will operate properly over all G.711 (VoIP) networks. Before you deploy faxes, test the fax within the network to verify reliable operation.Call Server Settings:
Check the following settings for fax and/or modem stations connected to an analog line card in a media gateway:
1. Media Gateways (Element Manager):
- Enable Modem/Fax Pass Through
- Enable V.21 FAX tone detection
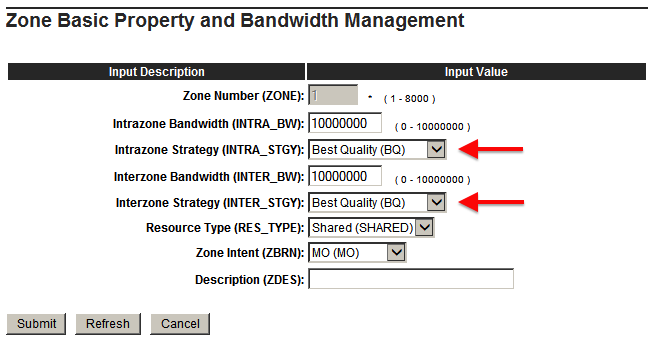
- MGC's (and VGW trunks) should be in a Zone with Best Quality (BQ)
2. Station Class of Service (LD 10):
- Both: CLS FAXA. Fax allowed. ISDN call is generated with 3.1 KHz Bearer Capability. Set is a modem or a FAX machine.
- Faxes: CLS MPTD. This setting will allow lower speed faxes (up to 14.4) to use T.38, and higher speed faxes to use G711 clear channel (no echo cancellation, no nonlinear DSP features).
- Modems: CLS MPTA. This setting will force all calls to use G711, supporting rates up to 33.6 kbit/s (eg: for data modem 'devices').
Additional Note:
- Digital trunk routes (LD 16, RDB) should be set to DSEL 3VCE for voice and data/fax applications. The default is VOD, and sometimes problematic with data/fax.